In patient surveys on insulin dosing, patch pumps score significantly better than conventional insulin injections in terms of comfort and user-friendliness. They are easy to use, comfortable to wear, and do not need to be removed for sports, showering, etc. For safe and comfortable handling, it is essential that the patch pump doses the insulin precisely and evenly. The micropumps developed at Fraunhofer EMFT achieve dosing deviations of less than 4% even with the smallest volumes. Researchers at the institute were able to verify this in a study.
Study on optimized insulin dosing with micropumps
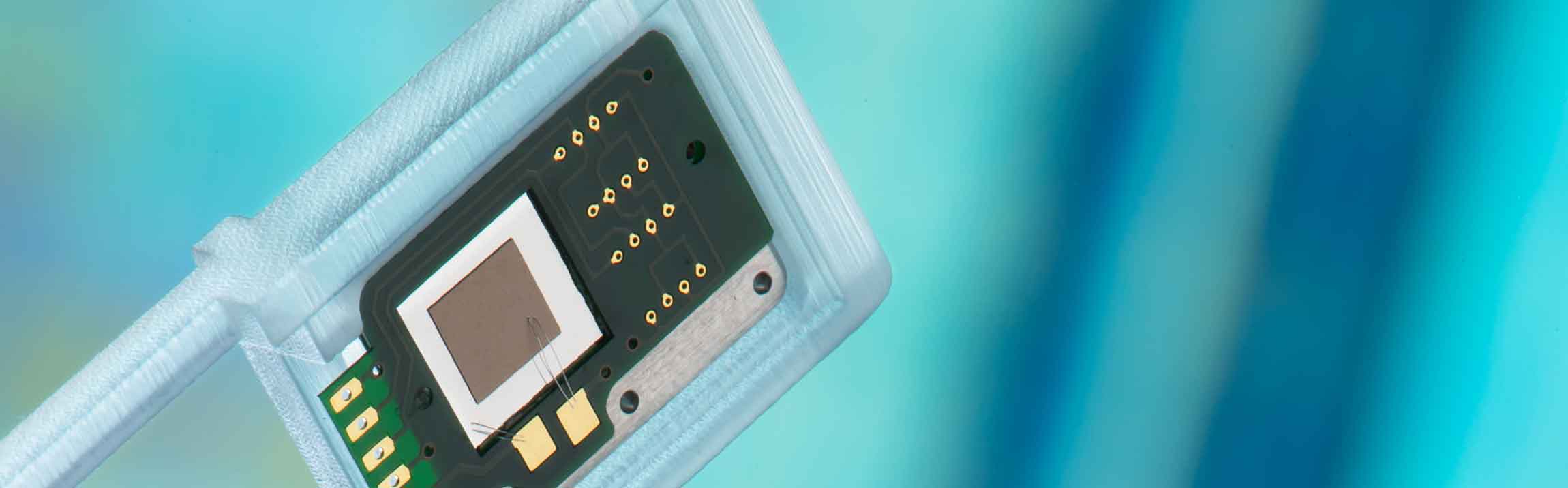
In terms of miniaturization, dosing accuracy, backpressure capability and bubble tolerance, the micropumps developed at Fraunhofer EMFT are ideally suited for use in such patch pumps. However, another aspect is crucial for the actual application in the product: the interactions between the pump and the medium to be dosed. The reason for this is that different media demand very specific requirements of the pump. As part of the internal "Smartpump" R&D platform, Fraunhofer EMFT researchers are systematically investigating the interaction between micropumps and media relevant to medical technology.
Insulin, for example, causes higher dosage deviations than water, because more robust bubbles are formed due to the higher surface tension. Experience with existing insulin patch pumps confirms this: For example, some diabetes patients report problems adjusting their blood glucose when they reattach a pump. This suggests that there is a kind of run-in process and that the dosing rate first has to stabilize in the first few hours.
High accuracy right from the start
The research team's goal, therefore, was to test their micropump without break-in to demonstrate that high accuracy can be achieved from the start. To this end, insulin doses were examined in individual "volume packages." Very small volumes of liquid can also be set, as the micropump's small dimensions allow very fine graduation of the desired volume. By switching the pump's electrical control on and off, the dosing time and thus the package size can be adjusted. The team tested the repeatability with Fraunhofer EMFT micropumps in each case with water and insulin and for three different package sizes. Even with the smallest amount of just 0.5 mg, they were able to dose the insulin extremely accurately using this approach - the variation was less than 4 %. Such exact dosing accuracy is the basic prerequisite for using higher-concentration insulin in the pumps in the future. The advantages: The lower volume would further reduce the reservoir size or the size of the entire patch pump system, thus further increasing patient comfort.